Things that connect with each other, exchange information and generate automatic actions based on data. That’s the Internet of Things (IoT). And in case this definition per se is not fascinating enough, in this article we have compiled a lot of examples of IoT devices and their uses that will make you realise the potential of this technology.

What is IoT?
The Internet of Things refers to any object that connects and shares information and data over the Internet.
The idea is simple, but its power is not what can already be done with it
Its power lies in the limitless possibilities that this technology brings and that will become more and more sophisticated through trial, error and imagination.
IoT is a technological trend that will be continuously and unstoppably evolving.
Types of IoT devices
IoT devices use a variety of technologies – wireless and Bluetooth technologies, NFC, LTE, ZigBee, wireless protocols, and so on. But probably almost everything we call “smart” has IoT technology associated with it.
In fact, there are different types of IoT devices depending on the complexity of their functionalities or their widespread use.
Based on how sophisticated they can be, we can classify IoT devices as follows:
- Devices capable of imitating behaviours or decisions predefined by humans. In other words, simply automating processes and actions based on parameters entered by a person.
- Or devices capable of defining new rules, making decisions and testing actions based on collected data. In other words, IoT devices in conjunction with artificial intelligence, machine learning or neural networks.
If we talk about the major uses of IoT devices by sector, then we can talk about five types of IoT devices:
- IoT for consumption: i.e. for everyday use: home automation, voice assistants, etc.
- Commercial IoT: Typical in the health sector or the transport industry. For example, a smart cardiac pacemaker or a parcel tracker.
- Military IoT (IoMT): surveillance robots, biometric wearables to monitor people in the field, etc.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): typical uses in the manufacturing and energy sector, e.g. with digital control systems, smart agriculture and industrial data analysis.
- IoT and infrastructures: e.g. to create smart cities, smart buildings etc. With all kinds of measurement sensors and control systems, incidents, predictive maintenance, etc.

Is IoT a trend? Where is the real value of IoT devices?
IoT devices are a mine, not of gold, but of data.
Using the data collected and processed by IoT devices is at the heart of many business optimisations … and life.
For example, by correctly reading the data provided by IoT devices in a business, industry or city, it is possible to predict failures, reduce the time to find solutions to possible errors and increase automation.
In other words, reducing costs in ways that have not yet been discovered.
In addition, data from IoT devices also translates into undiscovered business opportunities. For businesses and cities to continue to grow and create wealth.
That’s why you can’t talk about IoT without talking about data analytics.
Installing an entire IoT infrastructure without a system to manage and analyse the data generated and propose improvements is foolish.
It would be like ploughing a field, planting corn, harvesting it and then throwing it away.
Or like your Fitbit telling you how many steps you have walked, but not how many are many or how many are a few, 200? 2000? 2000? 20000? How many steps do other people like me take? What do the experts recommend?
Without good data management and analysis, all the information collected by IoT devices lacks context. And purposeless.
Advanced analytics with Big Data, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning, etc. techniques. It is the other side of IoT technology and anyone who wants to benefit from it needs to reinforce it with data analysis.
In fact, this concept already has a name: it has been dubbed the Internet of Behaviour (IoB).
At neuroons we already work with industrial companies to help them get value from their IoT devices deployed in buildings, factories, warehouses…etc. If you want to know how we do it with other companies, contact us.
Industrial IoT devices
IoT in retail
IoT devices are used to improve the shopping experience for retail customers:
- Improving stock management in warehouses.
- Personalising shopping experiences.
- Optimising the arrangement of products in spaces to improve sales, based on demand data analytics.
Application of predictive models that guide demand based on consumer preferences.

IoT in Industry 4.0 (IIoT)
It is one of the areas with the greatest potential for improvement through IoT technologies. Examples of real-life applications of IoT in the industry include:
- Predictive maintenance
- Real-time process monitoring and adaptation to the circumstances of production and logistics, minute by minute.
- Implementation of process improvements based on actual usage data obtained from IoT devices.
- Process optimisation and advanced data analytics.
- Detection of pressure build-ups and small leaks of hazardous chemicals (this can be fixed before they become serious problems).
- Generation of alarms, messages and triggering of automatic protocols to optimise resources such as energy or security.
- Detection of falls in warehouses and industrial centres and improvement of workplace safety. Reduction in the number of lawsuits filed against companies for this cause.
- Industrial security and safety: IoT-enabled detection systems, sensors and cameras can be placed in restricted areas to detect intruders.

IoT in transport
Intelligent Transport Systems benefit from these IoT solutions:
- Smart ports: the use of sensors in ports facilitates a constant process of increased speed, efficiency, sustainability and cost control.
- Real-time monitoring of the fleet: status, location, incidents…
- Monitoring and obtaining capacity and load flow data to maximise business.
- More efficient routing and reduced vehicle downtime: anticipating unforeseen events, bottlenecks, etc.
- Package tracking to improve the security and confidence of the receiver of the goods.

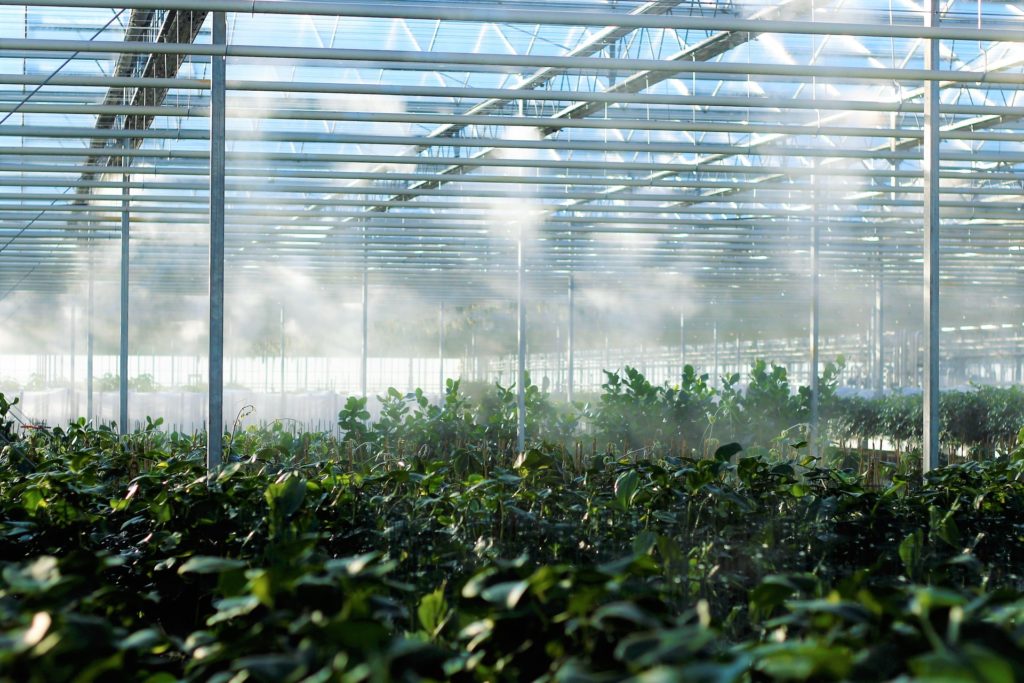
Smart Agri & Livestock: IoT in agriculture
This is how IoT applications in agriculture and livestock farming can help increase the efficiency and profitability of farming professionals:
- Knowing the state of the soil, weather conditions or humidity.
- Know nutrients that affect the crop or orchard.
- Determine the best time to harvest the plants.
- Create customised fertilisers based on specific soil chemistry.
- Detect endemic pests or problems.
- Biometric monitoring of animals.
- Geolocation of animals.
- It helps farmers to know in advance the volume and quality of yields and their vulnerability to unfavourable weather conditions, optimise water and nutrient supply for each crop, and even select yield traits to improve quality.
- Smart greenhouses: The adoption of IoT in greenhouses has eliminated human intervention, making the whole process cost-effective and increasing accuracy at the same time. These sensors help provide information on pressure, humidity, temperature and light levels, and allow automatic adjustment of temperature conditions, irrigation etc.

Smart Cities & Smart Buildings
- Smart people: citizens as a city sensor network to detect problems such as congestion or breakdowns.
- Air quality monitoring.
- Smart Environment: monitoring and optimisation of the use of natural resources (water, gas, electricity, etc).
- Structural motion detection: Motion sensors can detect vibrations in buildings, bridges, dams and other large-scale structures. These devices can identify anomalies and disturbances in structures that could lead to catastrophic failure. They can also be used in areas susceptible to flooding, landslides and earthquakes.
- Smart roads: traffic lights that are activated according to traffic flow or pedestrian crossings that automatically detect the presence of people, light up, signal the pace of crossing, etc.

IoT in Healthcare: Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
IoT medical devices can help monitor patients in real-time and remotely. They can inform a doctor in real-time of an emergency such as an asthma attack, heart failure, etc.
This can help save the lives of many people.
They can also collect and process health data such as blood pressure, sugar levels, oxygen and weight.
The data is stored online and can be accessed by the doctor at any time. Even when combined with AI processes, the algorithms themselves can detect health problems without going through a doctor first.
In addition to users, hospital facilities can benefit from the same IoT device applications for smart buildings.
Uses of IoT devices for everyday life
Another very suitable scenario for IoT solutions is home automation, where there are already numerous devices that connect to the internet to make life easier for humans.
But there are many other examples and applications of IoT for everyday life:
- Geolocation devices relate to each other by triangulating the signal of another device to locate it. Commercially, a clear example is the Apple tag. For example, to locate a lost dog in a park.
- Sensors to detect gas leaks in the home or faulty electronics.
- Home security: sensors, lights, alarms and cameras that can provide 24×7 security.
- Pet monitors: It can help you connect and see how your pet is doing, interact, dispense treats, schedule feedings…
- Smart locks: for example, you could open your front door for the Amazon delivery person when you are not there to pick up the package and trigger a security camera recording while the operation is in progress.
- Activity and health trackers. Sensors that can monitor and transmit health indicators such as your blood pressure, appetite, physical movement and oxygen levels. They could even warn you of cardiac abnormalities before a serious episode occurs.
- Indoor air quality: For example with products such as Foobot, an IoT device that can measure indoor pollution. It helps to improve air quality or clean up germs in homes, cafes, workplaces and other indoor spaces.
- Road safety: the installation of breath alcohol detection devices inside vehicles, which block the ignition if the permitted levels are exceeded, will become a legal reality in countries such as Spain.
- Connected household appliances: the robot hoover that does not crash or the fridge that predicts the expiry dates of products when to buy them again. Another example is the microwave that activates and heats up food when the user leaves work for home.
- Smart clothing: a pair of trainers that counts all the kilometres a person runs or a smart T-shirt capable of managing sweat during physical activity. For example, the use of suits that reuse bodily fluids in the film Dune.

IoT and Blockchain: example of the IoT helium network
The people’s network is a good example of new uses of IoT technologies that combine perfectly with other technologies, such as blockchain.
The Helium Blockchain network is a new blockchain built from scratch to incentivise the creation of decentralised, public wireless networks. People place a device in their homes, which, triangulated with other devices, receives and sends signals from other IoT devices distributed around the city, from products such as scooters, water or light sensors, geolocators, etc.
Security of IoT devices
The benefits of an Internet of Things network are many, but the risks of data sharing on the internet are a reality that we cannot ignore.
Among the obstacles to IoT deployment is reluctance over security issues.
The connection protocols between devices and the storage of data must be subject to the same security measures as any other industrial or commercial process in the cloud where people’s data are at stake.
This is why any IoT strategy has to be accompanied by a strong and sustained cybersecurity strategy.
Even when personal data is involved, techniques that enhance data security can be applied, such as the one anonymisation and pseudonymisation used by the company Nymiz.
In any case, this process of communication between devices and network is where the IoT is evolving the most.
Today, there are new devices whose communication and connection are easy, but they coexist with older, non-standard devices whose communication and connection protocol is divergent. And this gap needs to be bridged.
In addition, each manufacturer has its own communication protocols which means that not all devices are compatible.
For this reason, one of the mechanisms that have been tried to be established is the creation of an open and standard protocol that allows its use by all manufacturers, thus facilitating communication between different types of devices.
And along with these advances in communication between devices and the network, security measures for collecting, sending and storing data are increasingly developed and sophisticated.
All systems using the cloud can have a cyber-attack, but cyber-security systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated and IoT technology will benefit greatly from these developments.